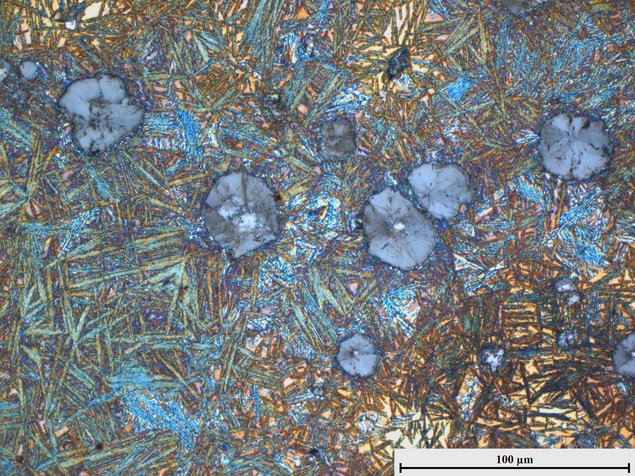
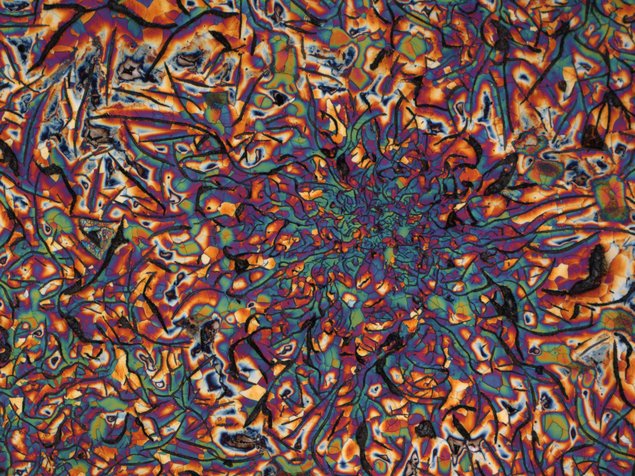
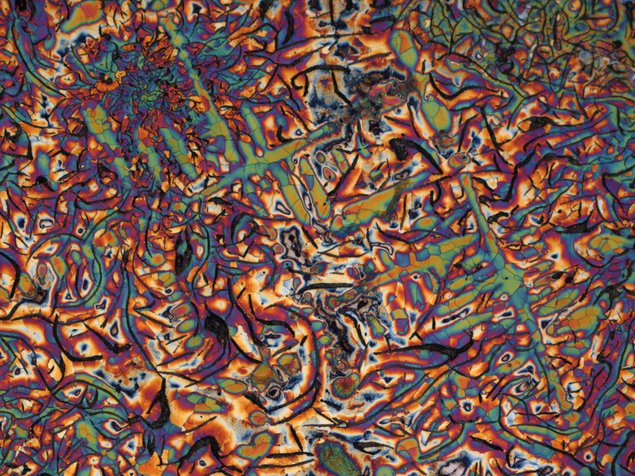
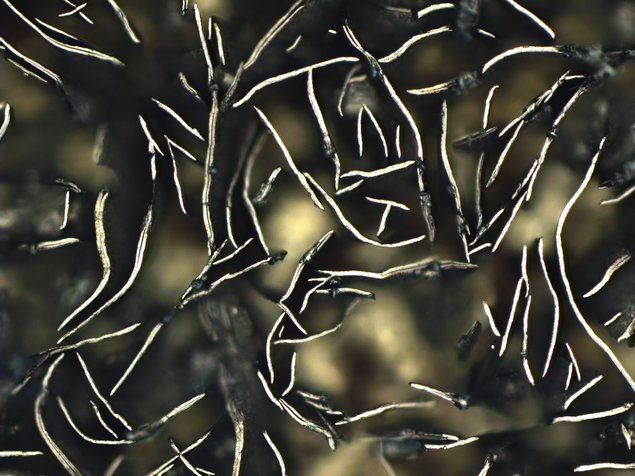
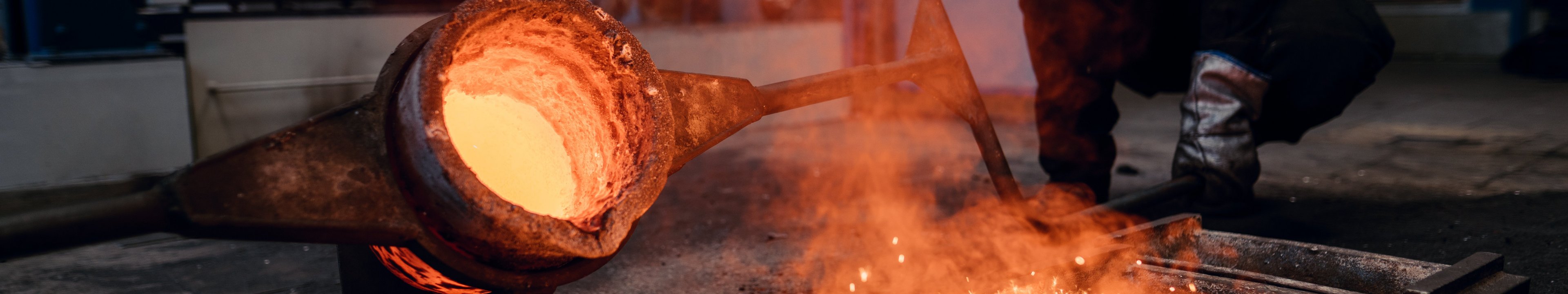Metallurgy is the engineering science of extracting metals from ores, of shaping metals by casting and forming processes and of recycling processes, according to which used metals, alloys and residues are retained in the business cycle. For all its diversity and versatility, metallurgy belongs on an orderly, scientific basis, which is certainly made up of physics, chemistry and mathematics.
The scientific penetration of processes in metallurgy has reached a high level. On this basis, sub-processes are mathematically modeled in the current development and the sub-processes are combined into simulation models.
The metallurgical industry in the Federal Republic of Germany has a very high, in some cases world-leading level of production and plant technology. Innovative developments have originated here. The predominantly medium-sized foundries supply practically all branches of industry. The international cooperation in metallurgy is remarkable.
Metals can be used as often as required in the metallurgical process. The technology of recycling metals and molding materials has been used for centuries and has been excepted and sold in recent years. In this way, companies in the metallurgy and scrap industry have set an example.
The economical use of raw materials and energy is a key issue in metallurgical development.